login2le@gmail.com +91-9272111897, +91-9168129688
- Send SMS Send Email
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Exporter, Supplier |
| Brand Name | MILTON |
| Country of Origin | India |
Preferred Buyer From
| Location | Anywhere in India |
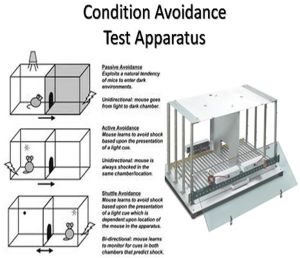
The Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) is a widely used behavioral test in pharmacology and neuroscience research to assess anxiety-related behaviors in rodents, typically mice or rats. Here's how it is used and its significance: Assessment of Anxiety: The primary use of the EPM is to evaluate anxiety levels in rodents. The maze consists of two open arms and two closed arms, elevated above the ground. Rodents naturally prefer enclosed spaces and avoid open, elevated areas due to fear of falling and exposure. Thus, the time spent in the open arms versus the closed arms serves as an indicator of anxiety levels. Testing Anxiolytic and Anxiogenic Compounds: The EPM is used to screen the effects of pharmacological agents on anxiety. Anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) drugs typically increase the time rodents spend in the open arms, indicating reduced anxiety. Conversely, anxiogenic (anxiety-inducing) substances reduce the time spent in open arms. Behavioral Profiling: The EPM helps in profiling the behavioral effects of various compounds. Researchers can observe changes in exploratory behavior, risk assessment, and overall activity levels, which provide insights into the drug's impact on anxiety and related behaviors. Mechanistic Studies: By using the EPM in conjunction with pharmacological manipulations (e.g., using receptor antagonists or agonists), researchers can investigate the underlying mechanisms of anxiety and the role of specific neurotransmitter systems, such as serotonin, GABA, and glutamate. Genetic Research: The EPM is used to study the genetic basis of anxiety by comparing the behavior of different rodent strains or genetically modified animals. This can help identify genetic factors that influence anxiety and contribute to our understanding of anxiety disorders. Longitudinal Studies: Researchers use the EPM to conduct longitudinal studies on the effects of chronic drug treatment, stress, or developmental changes on anxiety. This helps in understanding how these factors influence anxiety over time. Validation of Animal Models: The EPM is an essential tool for validating animal models of anxiety disorders. By showing that certain genetic, environmental, or pharmacological manipulations lead to anxiety-like behaviors in the EPM, researchers can establish the relevance of these models to human anxiety conditions. Behavioral Phenotyping: The EPM is part of a battery of behavioral tests used for phenotyping rodent models, particularly in studies investigating the impact of neurological or psychiatric conditions. It provides valuable data on how these conditions affect anxiety-related
Looking for "ELEVATED PLUS MAZE FOR RAT & MICE" ?
Explore More Products