login2le@gmail.com View Mobile Number
- Send SMS Send Email
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Exporter, Supplier |
| Brand Name | MILTON |
| Country of Origin | India |
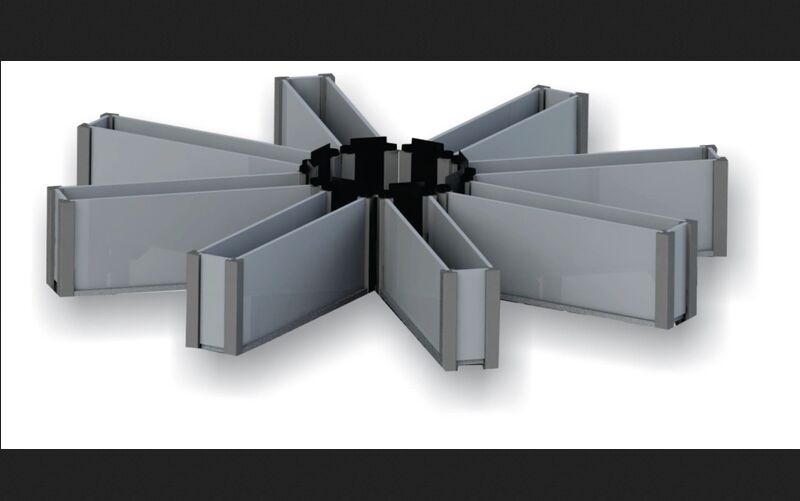
The Radial Arm Maze (RAM) is a widely used behavioral test in pharmacology and neuroscience research to study spatial learning and memory in rodents, typically rats and mice. Here are the primary uses of the Radial Arm Maze in pharmacology research: Assessment of Spatial Memory: The RAM is designed to evaluate an animal's ability to remember and navigate to specific arms to obtain rewards (usually food). The maze typically consists of multiple arms (often eight) radiating from a central platform. Successful navigation with minimal errors indicates good spatial memory. Studying Learning Processes: Researchers use the RAM to study the learning processes in rodents. By repeatedly testing animals over several trials, researchers can assess how quickly and efficiently the animals learn to remember the locations of the rewards, providing insights into the cognitive processes involved in learning. Evaluation of Cognitive Enhancers: The RAM is used to evaluate the efficacy of cognitive enhancers, such as nootropic drugs. These substances are tested for their ability to improve learning and memory performance in the maze. Improved performance after drug administration suggests potential cognitive-enhancing effects. Assessment of Cognitive Impairment: The RAM is also used to model cognitive impairments associated with conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, aging, schizophrenia, and other neurodegenerative or psychiatric disorders. By observing deficits in maze performance, researchers can study the underlying mechanisms of these conditions and evaluate potential treatments. Pharmacological Studies: The RAM is employed to investigate the effects of various pharmacological agents on cognitive functions. Researchers can study how different classes of drugs, such as cholinergic agents, glutamatergic modulators, or neuroprotective compounds, influence spatial memory and learning. Neurobiological Research: Using the RAM, researchers can explore the neurobiological mechanisms underlying learning and memory. This includes studying the role of specific brain regions (e.g., hippocampus, prefrontal cortex), neurotransmitter systems, and signaling pathways involved in cognitive functions. Genetic Studies: The RAM is used to assess the impact of genetic modifications on cognitive abilities. By comparing the performance of wild-type and genetically modified animals, researchers can identify genes that play critical roles in learning and memory. Longitudinal Studies: The RAM allows for longitudinal studies to assess how cognitive abilities change over time in response to aging, chronic drug treatment, or environmental factors. This helps in understanding the progression of cognitive decline and the long-term effects of interventions. Behavioral Phenotyping: The RAM is part of a comprehensive battery of behavioral tests used for phenotyping rodent models. It provides valuable data on the cognitive phenotype of different strains or genetically engineered models, contributing to a better understanding of the genetic basis of cognitive functions.
Looking for "EIGHT RADIAL ARM MAZE FOR RAT & MICE" ?
Explore More Products